Junk & Phishing
Microsoft 365 has a variety of security features that help protect you from email-based cyber attacks.
Anti-Phishing Protections
Phishing emails are a form of cyber attack that attempts to steal user data. This data may include:
- Your email address and password
- Your identity
- Information about the company you work for, e.g. reporting structure, commonly contacted people and their information
The Microsoft 365 spam filter detects potential phishing emails and will move them to your junk folder.
In addition, it will flag potential phishing emails and tell you why it has been identified as such.
Domain Spoofing
A domain name is your organisation's website address and the part of your email address after the @. It identifies your organisation.
Some phishing emails try and pretend to be an official email from your organisation by inserting your organisation's domain name into the From name or subject line of an email. If this is detected in an email and the contents of the email look suspicious, Microsoft 365 will insert a message to warn you as such. Here's an example:
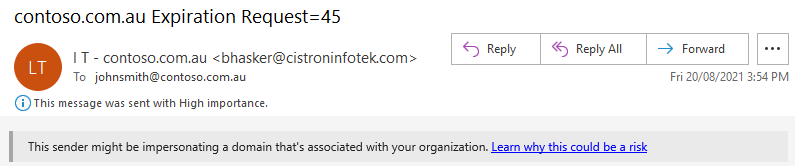
In the example above, the organisation's domain name is "contoso.com.au". Microsoft 365 has detected that "contoso.com.au" is present in the subject line (as well as the From name) and marked the email as a potential phishing attempt.
When you see this warning, carefully check if the contents of the email are legitimate before clicking on any links or opening any attachments. If in doubt, contact the Private Universe Helpdesk and we will review it for you.
If you have confirmed that the emails are illegitimate, you should delete these emails from your junk folder.
Sender Spoofing
Some phishing emails will pretend to be an individual that you know. The From name contain that person's name, despite the actual From address being incorrect.
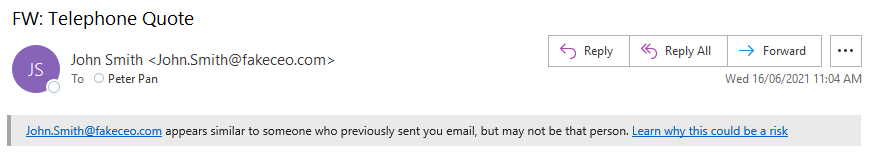
In the example above, Peter Pan has received an email from the sender "John Smith". However, the name "John Smith" matches another person with a different email address that has previously sent email to Peter Pan.
In situations like this, it is important that you check that the sender's email address is correct. If the sender's email address differs from that person's usual email address, it may be a phishing attempt.
If you are unsure if the email is legitimate, contact the person using other means (such as a phone call) to check if they sent the email to you. Do not reply to the email.
In some cases, the email may also mimic the style of the real individual and their email signature. If you receive a phishing email from someone you know and it contains their email signature, it is likely that their email account has been compromised. You should consider informing them of this email using other means, such as a phone call.
If you receive a phishing email from someone within your organisation and it contains their email signature, it is likely that their email account has been compromised. Please immediately inform them as well as the Private Universe Helpdesk so that we can investigate and secure the account.
If you receive a legitimate email and it has been incorrectly flagged as a potential spoofing attempt, please forward it to the Private Universe Helpdesk. We will assess the email and add the sender to an allow list if appropriate.
First Contact
The first contact safety tip supplements the sender spoofing protections by identifying emails that you may receive from senders who don't often send you emails. Many phishing emails will come from fake email addresses.
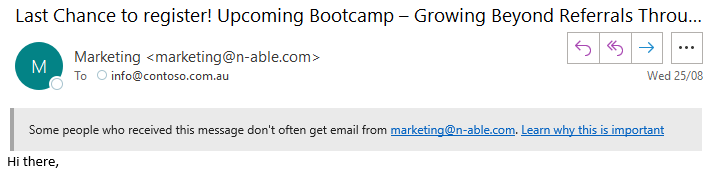
If you see this "don't often get email" warning, you should be wary of who the sender is and consider if the email is authentic.
If you see this message in a genuine email, there is nothing to worry about - it is simply a warning. Microsoft 365 will learn that it is a legitimate sender over time and the warning will stop appearing.
Reporting Messages
Spam filters are not always perfect. They may incorrectly identify spam messages as clean and vice versa as techniques used to send spam emails evolve regularly.
Phishing Messages
Phishing messages are different to usual spam messages. As described under Anti-Phishing Protections, phishing messages seek to steal user data.
If you have received a phishing message in your inbox, it has not been correctly identified. Use the Report Message button in Outlook to report it was one to help train the spam filters.
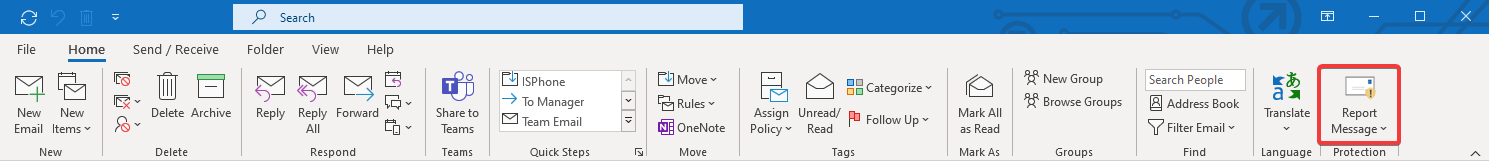
- Click on the Report Message button
- Select Phishing
The message will then be moved to your junk/spam folder where you can safely delete it.
False Positives
If you believe you have received an email that was incorrectly flagged as spam, this is known as a false positive. Use the Report Message button in Outlook to report it as such. This will help improve the spam filters.

- Click on the Report Message button
- Select Not Junk
- Click Report in the window that opens
The message will then be moved out of your junk/spam folder into your Inbox.
False Negatives
If you believe you have received an email that should have been flagged as spam but landed in your inbox, this is a false negative. Use the Report Message button in Outlook to report it to Microsoft so that it contributes to the ongoing development of spam filters.

- Click on the Report Message button
- Select Junk
The message will then be moved to your junk/spam folder where you can safely delete it.